Website indexing is an extremely important part of search engine optimization (SEO). It’s essential to ensure that search engines can index your site. If not, your site won’t rank in search results, and you’ll miss out on traffic, leads, and conversions as a result.
That’s why we’re bringing you this complete website indexing 101 guide to cover everything you need to know. Let’s get started!
- What is website indexing
- 9 best practices for getting indexed
- 4 reasons why your site isn’t getting indexed (and how to fix it!)
What is website indexing?
Website indexing is the process of search engines identifying web pages on the Internet and storing the data from those pages in their database in order to consider the pages for rankings in future search results.
You can think of indexing like a bookshelf. A search engine like Google discovers a book (a web page) and adds it to its bookshelf (its database). Then, when someone searches for a topic (a search query), Google can choose a handful of books (search results) to give to them.
Your website must be indexed by search engines in order for your pages to rank in the search results.
Make Complex SEO Simple
How does website indexing work?
Search engines use crawlers, sometimes known as search engine bots or spiders, to crawl web pages on the Internet. When a search engine crawler finds a page, it stores essential information about it, like its copy, title, and meta description, and sends that information to the search engine.
The search engine then indexes the web page by storing that information in its database. It will then use the pages in its database to deliver relevant websites in the search results when a user enters a query.
If a search engine crawler can’t crawl your page or website, it will prevent search engines from indexing it, which means your site won’t rank in the search results.
9 best practices for getting indexed
How do you ensure search engines index your pages? Ultimately, it all comes down to making your site easy for search engines to crawl your site. There are lots of ways to do this, but following these nine best practices for getting indexed are the first place we start!
- Submit your sitemap to Google
- Add internal links throughout your website
- Ensure your content is worth indexing
- Ask Google to index individual URLs
- Optimize your page load speed
- Improve your server response time
- Remove duplicate content
- Find and fix broken links
- Reduce redirects on your site
1. Submit your sitemap to Google
One of the best ways to ensure your pages get indexed is to submit your sitemap to Google. By submitting your sitemap, you essentially give Google an entire roadmap of your site along with each and every one of your URLs.
That means Google can identify and index your pages easily.
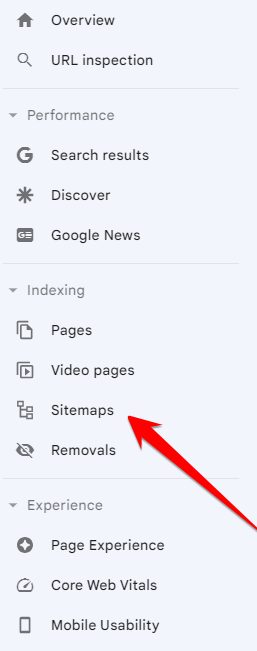
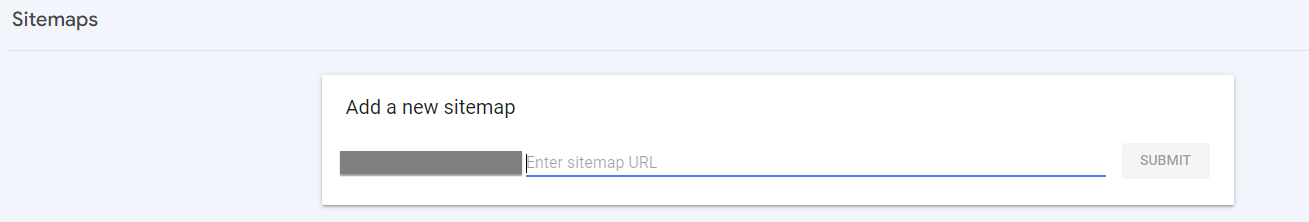
To submit your sitemap to Google, follow these steps:
- Head on over to Google Search Console
- Click on Sitemaps under Indexing from the left sidebar menu
- Enter your URL
- Click submit
2. Add internal links throughout your website
Search engine spiders crawl websites by passing between links on pages. And like we mentioned before, search engine spiders must be able to crawl your site in order for search engines to index your pages.
That’s why it’s essential to add internal links throughout your website. Without them, it’s difficult for web crawlers to accurately crawl and index your pages.
You can add a few types of internal links:
- Navigational: Navigational links appear in your navigation or footer.
- Sidebar: Sidebar links appear in right- or left-hand sidebars or at the bottom of content.
- Contextual: Contextual links appear within your written content.
Aim for your content to have three to five internal backlinks. Your most important URLs should have navigational links to demonstrate their importance to Google, plus make navigating your website as easy as possible for users.
3. Ensure your content is worth indexing
The main goal of any search engine is to provide its users with a great experience. And to do so, the search engine needs to show relevant and helpful content that answers its users’ questions and gives them the information they need.
If search engines don’t think that your page is helpful or valuable to users, it might not index your page, even if you’ve submitted a sitemap. Pages with little content or pages that merely link to other pages on your site (like your blogs pagination) are frequently ones search engines skip indexing.
Here are a few tips to help you write high-quality, valuable content:
- Write for people, not search engines
- Provide original information, reports, and research
- Provide a complete and comprehensive description of the topic
- Write descriptive titles that accurately summarize the topic of your page
- Showcase your expertise or industry knowledge
4. Ask Google to index individual URLs
Next on our list of website indexing best practices is to request indexing from Google. That’s right. You can simply ask Google to index your URL.
And it’s pretty easy to do, too.
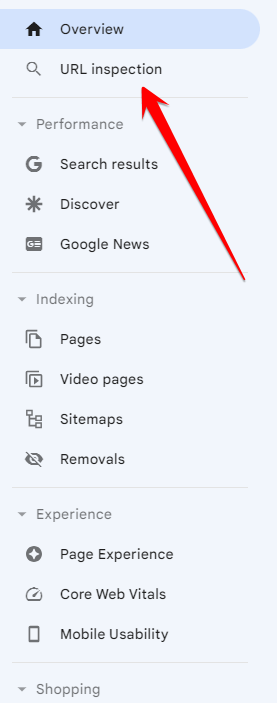
Here’s how to request indexing from Google:
- Navigate to Google Search Console
- Click on the URL inspection tool from the left sidebar menu
- Enter the URL of the page you want to be indexed
- Click Request Indexing
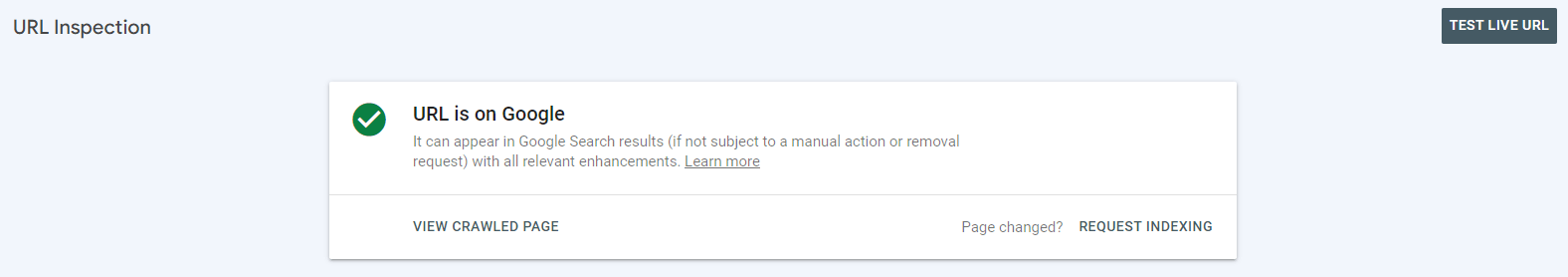
If there is a reason Google will prefer to skip indexing this particular page, it will often tell you why. Sometimes it’s a simple technical issue standing in your way of indexing the page, and Google will let you know in the details.
5. Optimize your page load speed
Believe it or not, search engine crawlers don’t actually have all day to crawl and index your pages. Web crawlers stick to a crawl budget — the number of pages search engines will crawl on a website within a certain timeframe.
If your website takes too long to load, web crawlers may run out of time to crawl and index all of your pages.
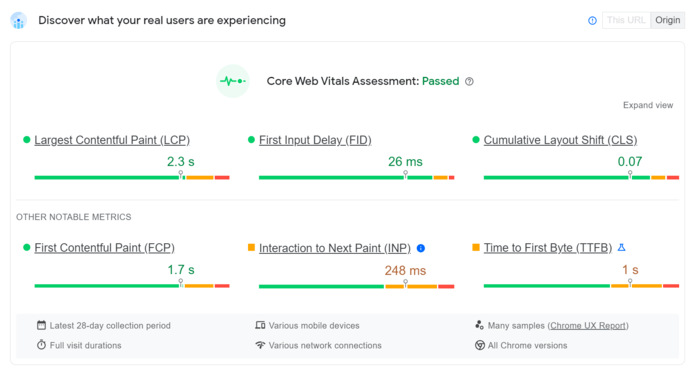
That’s why it’s essential to ensure that page load speed is as fast as possible so that search engines can successfully index all of your pages.
Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool to quickly view your site’s current load time as well as recommendations to improve your load speed.
6. Improve your server response time
All the crawling from search engine spiders can take a toll on your website, so having a high-performing server is important.
If your server response time is slow or is subject to consistent errors, search engine spiders may have a difficult time crawling and indexing your website.
Use Google Search Console’s Host status report to check your server response time easily. We recommend aiming for a response time less than 300 milliseconds.
7. Remove duplicate content
Duplicate content confuses search engine crawlers and can cause them to not index the correct page. That’s why removing duplicate content is next on our list of website indexing best practices.
You can quickly find duplicate content by navigating to your Crawl Stats report in Google Search Console and looking out for duplicate tags. Then, remove any cases of duplicate content you find to best optimize your website for search engine crawling and indexing.
8. Find and fix broken links
Broken links cause errors and can also confuse search engine crawlers, making it more difficult for them to crawl and index your URLs.
Finding and fixing these broken links as quickly as possible is a good idea to avoid any indexing issues.

“Google’s indexing pipeline doesn’t consider URLs that return a 4xx status code for indexing, and URLs that are already indexed and return a 4xx status code are removed from the index.”
Use a tool like Screaming Frog or Google Search Console’s Crawl Stats report to easily find 404 errors on your site. Once you find them, be sure to either redirect those URLs, update them, or remove them completely from your site.
It’s also good practice to set up a time to regularly check your site for broken links so that you can fix them quickly.
9. Reduce redirects on your site
Redirects are common, and almost every website out there uses them. But that doesn’t mean they don’t come with their own batch of problems.
If you’ve changed the URL on one of your main pages, but haven’t updated the links pointing to it, you’ll find that Google has a harder time indexing the updated URL.
On the other hand, it can be easy to make a mistake when it comes to redirecting URLs, and search engine crawlers won’t react well to them.
Redirects direct users from one page on your site to a newer or more relevant one. One of the most common mistakes with using redirects is to accidentally create a redirect loop. A redirect loop happens when you direct users to one page, and then that page directs them to another page, and so on.
It’s confusing for both users and search engine crawlers and can cause search engines to incorrectly index your pages.
Use a tool like Screaming Frog to view a report of your site’s redirects, check that each one directs users to a relevant page, and remove any redirect loops.
Make Complex SEO Simple

4 reasons why your site isn’t getting indexed (and how to fix it!)
Not sure why search engines aren’t indexing your site?
Here are four common reasons why your content isn’t getting indexed and how to fix it!
- Your site isn’t optimized for mobile users
- Your content doesn’t adhere to Google Search Essentials
- You don’t have a sitemap
- Your robots.txt file blocks search engine crawlers from crawling your website
1. Your site isn’t optimized for mobile users
Ensuring your website is mobile-friendly isn’t just important to create the best user experience on your site, but also getting indexed by Google.
Google uses mobile-first indexing criteria — so even if you submitted a sitemap to Google and have valuable content on your site, it won’t matter much if your site isn’t optimized for mobile users.
How to fix it
Implementing responsive design for your website is one of the best ways to make your website mobile-friendly. It ensures that your site displays and functions correctly for users no matter what device they use.
If you aren’t sure whether your site is mobile-friendly, use Google’s Lighthouse report to quickly find out.
Sometimes it’s a stray image or incorrectly formatted element on your page that causes some mobile issues. It’s generally easy to patch these up so Google gives you the official green mobile-friendly checkmark!
2. Your content doesn’t adhere to Google’s webmaster guidelines
We mentioned earlier that Google wants to provide users with the best possible content — and that means showing them valuable, high-quality content that adheres to their webmaster guidelines.
If you aren’t checking the boxes for everything Google thinks your content should include or if your pages violate the guidelines, they won’t be indexed.
How to fix it
You can view the full list of Google’s webmaster guidelines here, but here’s a quick overview of a few key elements your content should include:
- Relevant keywords and phrases without keyword stuffing
- Links to your page from another findable page on your site
- Write content for people and not for search engines
- Follow Google’s best practices for using images, videos, and structured data in your content
3. You don’t have a sitemap
If you don’t have a sitemap or didn’t submit it to Google, this is probably the biggest reason why your site isn’t getting indexed.
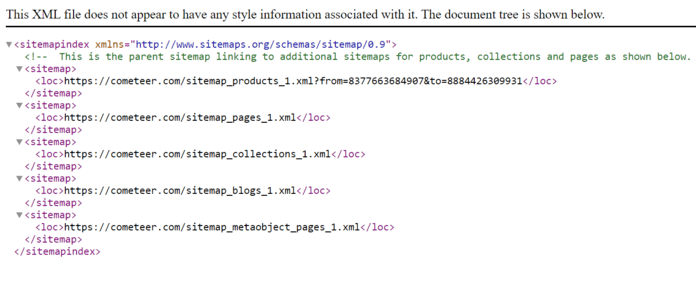
A sitemap is a list of all the pages on your site, and it’s one of the best ways for Google to learn about the content you have.
If your pages aren’t currently indexed or received traffic, and you haven’t submitted a sitemap to Google, Google essentially doesn’t know about your site.
How to fix it
Create a sitemap that lists out all of the URLs on your website and save it in a file. Navigate to Sitemaps in Google Search Console, upload your sitemap, and click submit.

“Create an XML sitemap file to ensure that search engines discover the new and updated pages on your site, listing all relevant URLs together with their primary content’s last modified dates.”
If you update any of your pages, it’s important to regularly submit your sitemap for crawling and indexing so Google always has an up-to-date list of the content on your website.
4. Your robots.txt file blocks search engine crawlers from crawling your site
A robots.txt file manages traffic from bots and prevents your site from being overrun with requests. This file can help you tell search engines how you want them to crawl your website.
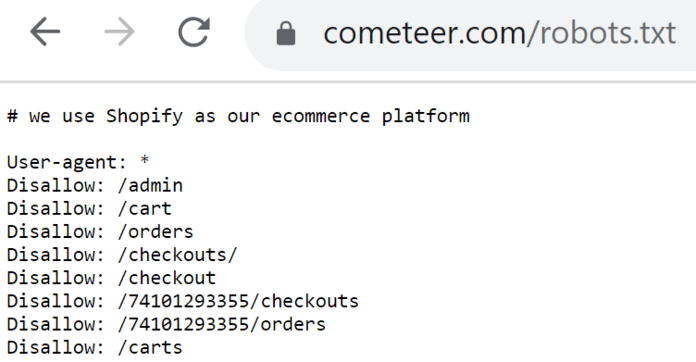
But they can be tricky.
If you’re finding that your site isn’t getting indexed, it could be because your robots.txt file blocks search engine crawlers from crawling your website.
How to fix it
The best way to fix and optimize your robots.txt file is to ask a technical SEO expert since it can be such a complicated process. At seo.com, we offer technical SEO services and have technical SEO specialists on hand ready to help fix your robots.txt file and ensure it’s optimized for website indexing.
Improve website indexing with SEO.com
Make sure your site can be found on search engines. Use SEO.com to audit your website, check your rankings, and find more SEO opportunities. Sign up and analyze your site in minutes! Try SEO.com for free today.
Make Complex SEO Simple


Make Complex SEO Simple
Identify indexing issues faster with SEO.com’s automated website audit tool that helps make complex SEO easier for new SEOs like you!
Writers




