Noindex tags provide the flexibility you need when managing multiple marketing channels, from search and paid to social and email. With noindex directives, you can optimize your search engine optimization (SEO) strategy by excluding non-SEO pages from appearing in organic search results.
Learn more about the meaning, benefits, use cases, and setup of noindex tags below!
What is a noindex tag?
A noindex tag is a <meta> tag or robots directive instructing search engines not to index an HTML or non-HTML resources, like PDF, image, or video files. Common use cases for noindex tags include landing pages and downloadable resources.
What is the difference between a noindex meta tag vs. robots noindex tag?
The difference between a noindex meta tag and a robots noindex tag is the installation and use cases:
Installation
- A noindex meta tag is installed in a URL’s <head> section, typically by an SEO.
- A robots noindex tag is installed in the HTTP header, typically by a web developer.
Use cases
- A noindex meta tag is used for HTML resources.
- A robots noindex tag is used for non-HTML resources.
Appearance
A noindex meta tag appears as follows:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta name="robots" content="noindex, follow">
<title>Your Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Your page content goes here -->
</body>
</html>
A robots noindex tag appears as follows:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Wed, 13 Oct 2023 00:00:00 GMT
Server: Your Server
X-Robots-Tag: noindex, follow
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
Content-Length: xxx
<!-- Your page content goes here -->
If you’re uncertain about which noindex directive you should use, look at what you’re looking to block from indexing. For HTML files, like a paid landing page, you’ll use a noindex meta tag. In comparison, for PDF, image, or video files, you’ll use a robots noindex tag.
Why is a noindex tag important in SEO?
A noindex tag is important in SEO because it allows you to manage your search visibility, like for:
- Landing pages, like for an ad or email campaign
- Thank you pages, like for a contact or ordering form
- Downloadable resources, like a PDF
Typically, you wouldn’t want these pages to appear in search results because they’re intended for a different purpose. For example, none are optimized for search, and some (like a thank you page) wouldn’t offer anything valuable to users searching on the Internet.
When should I use a noindex meta tag?
Besides using a noindex meta tag for HTML resources (you’d use a robots noindex tag for non-HTML resources), you’ll also use a noindex meta tag based on factors unique to your site and digital marketing strategy.
Some common page types for using a noindex tag include the following:
- Landing page
- A/B testing page
- Thank you or contact confirm pages
- Paginated pages
- Archive pages
While specific to SEO, noindex tags are a team effort. Collaboration is critical to learning about new pages, like a new landing page for pay-per-click (PPC), or resources, like a downloadable resource for driving email opt-ins via email marketing services, that shouldn’t get indexed by Google.
How do I set up a noindex tag?
Setting up a noindex tag starts with identifying which tag you’ll use:
How to set up a noindex meta tag
Learn how to set up a noindex meta tag (which is for HTML resources) below:
- Open the URL’s HTML file
- Add one of the following meta tags in the <head> section:
- To allow search engines to follow the URL’s links, use
<meta name="robots" content="noindex, follow"> - To prevent search engines from following the URL’s links, use
<meta name="robots" content="noindex, nofollow">
- To allow search engines to follow the URL’s links, use
- Save and upload the HTML file
If you use a content management system (CMS) like WordPress and a popular SEO plugin like Yoast SEO, you can add a noindex meta tag without using HTML. Just follow these steps:
- Open the URL’s editor
- Open the Yoast toolbar
- Click “Advanced”
- Select “No” from the dropdown menu labeled, “Allow search engines to show this Post in search results?”
- Click “Update” to save your changes
You can verify your work by visiting the URL and viewing its page source (use the shortcut Ctrl+U in Google Chrome). You can then search for “noindex” to see your noindex tag, which should appear near the top of the page in your <head> tag.
How to set up a robots noindex tag
Learn how to set up a robots noindex tag (which is for non-HTML resources) below:
- Open the site’s .htaccess file
- Add one of the following directives:
- To allow search engines to follow the URL’s links, use
X-Robots-Tag: noindex, follow - To prevent search engines from following the URL’s links, use
X-Robots-Tag: noindex, nofollow
- To allow search engines to follow the URL’s links, use
- Save and upload the file
In most cases, you’ll need to work with a web developer to implement a robots noindex tag.
5 best practices for your SEO noindex tags
While adding noindex tags to your website’s content is easy, noindex tags carry immense power in search engine optimization because they stop search engines from indexing content. That’s why it’s vital to review these best practices for SEO noindex tags:
1. Ask for help
If you’re unsure about implementing a noindex tag, ask for help. For example, if you’ve never worked with your site’s .htaccess file and need to set up a robots noindex tag, ask your web developer for assistance, whether to implement the tag or give a walkthrough.
2. Review search engine documentation
Following search engines and their changing documentation will keep you informed on their noindex tag policies. Google, for example, shared that even if you use “noindex, follow” in your noindex meta tag, Google will eventually stop following the links on the URL.
3. Test noindex implementations
Google provides a free, built-in tool in Google Search Console for testing your noindex tags. Use the URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console to see if Google’s crawlers saw the noindex directive when crawling the URL.
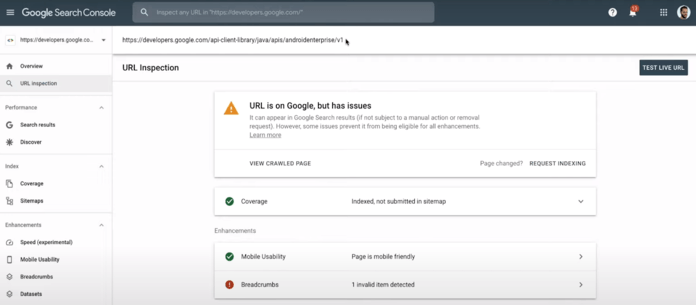
4. Request search engines to recrawl new noindex content
If you’ve currently applied the noindex tag to content in a search engine’s index, request a recrawl. You can do this from the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console. By recrawling your content, Google can discover your noindex tag.
5. Use canonical tags for duplicate content
While some SEOs recommend using noindex tags for duplicate content, it’s better to use canonical tags. A canonical tag explains to search engines which URL should rank, so if URL A’s canonical tag references URL B, Google knows its URL B that should get served in search results, not URL A.
Optimize your indexation with SEO experts
Indexation is critical to search engine optimization, which is why noindex tags are a vital part of learning SEO. If you want to continue building your SEO knowledge, browse our blog to read our SEO expert’s latest advice, tips, and tricks!
Don’t fail your website’s most important test
Get an SEO scorecard of your website for free in less than 30 seconds.
Let’s Drive Results Together 
Writers

Related Resources
- What is a 404 Error? Overview and How to Fix It
- What is a Cached Page? A Beginner’s Guide to Cached Web Pages in SEO
- What is a Canonical URL? Ultimate Guide to Canonical Tags
- What is a CMS? Your Guide to Content Management Systems
- What is a Search Crawler? Your Ultimate Guide to Search Bots
- What is a SERP (Search Engine Results Page)?
- What is a Sitemap? Definition, Uses, and Tips
- What is a URL Slug? Tips for Creating SEO-Friendly URL Slugs
- What is Alt Text? + How to Craft Effective Alt Text for SEO
- What is Click-Through Rate in SEO? [A Marketer’s Guide]


